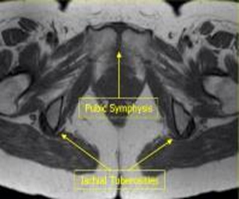
A sports hernia MRI protocol is a type of imaging technique used to diagnose a condition called sports hernia. This condition is generally caused by overuse of the lower abdominal muscles and can cause pain and discomfort in the area. An MRI is a powerful tool to help diagnose this condition, as it can provide a detailed look at the soft tissue structures in the area. The MRI protocol for sports hernia focuses on the lower abdominal muscles, and includes imaging of the lower abdomen, groin, and hips. It is an important part of the diagnostic process, as it can help determine the extent of the injury and provide valuable information to aid in treatment.
Definition of a Sports Hernia
Sports hernia is a term used to describe a tear in the lower abdominal wall or groin. It is not an actual hernia, and the term is used to describe a variety of conditions that can cause pain in the lower abdomen, groin, and pubic region. Sports hernia is caused by repetitive strain and overuse in sports-related activities, making it a common injury among athletes. Symptoms of a sports hernia include pain in the lower abdomen, groin, and pubic region, especially during and after exercise. Diagnosis of a sports hernia is usually made through physical examination and imaging tests such as an MRI. Treatment of a sports hernia typically includes rest, physical therapy, and medications. Surgery may be required in severe cases. The protocol for a sports hernia MRI involves an evaluation of the lower abdominal and groin muscles to identify any tears or abnormalities of the muscles and tendons. This protocol helps to confirm the diagnosis and determine the best course of treatment.
Causes of a Sports Hernia
Sports hernia is a debilitating condition that affects both professional athletes and weekend warriors. It is caused by the weakening of the abdominal wall muscles, which can lead to a tear in the abdominal wall. The most common cause of a sports hernia is repetitive strain on the abdominal wall from activities such as running, jumping, and kicking. It can also be caused by trauma to the abdominal wall, such as a fall or car accident. Other causes include a lack of stretching or warm-up exercises before strenuous physical activity, poor posture, and muscle imbalances.
It’s important for athletes to take preventative measures to reduce the risk of developing a sports hernia. Stretching before and after exercise can help to reduce muscle imbalances, and strengthening exercises can help to protect the abdominal wall from damage. Proper warm-ups and cool-downs before and after physical activity can also help to reduce the risk of a sports hernia. Additionally, athletes should take breaks throughout their workouts to ensure that they are not overworking their muscles. If an athlete experiences any pain or discomfort in their abdominal area, they should immediately stop their activity and seek medical attention.
Diagnosis of a Sports Hernia
When it comes to diagnosing a sports hernia, MRI protocols are the most useful. An MRI of the affected area can provide invaluable insights into the severity of the injury, allowing doctors to more accurately diagnose and treat the condition. The MRI protocol used to diagnose a sports hernia typically includes images of the affected area in both the standing and supine positions. This allows the doctor to assess the degree of disruption in the affected tissue. Other imaging techniques such as ultrasound and CT scans may also be used to supplement the MRI protocol.
The MRI images are used to measure the degree of tissue damage and identify the exact location of the hernia. In addition, they can also be used to detect any associated soft tissue injuries or structural abnormalities. The MRI protocol is also used to measure the range of motion and flexibility of the affected area, which can be helpful in determining the extent of the injury.
Once the MRI protocol is complete, the doctor can make a more informed diagnosis. With the help of this information, the doctor can determine the best course of treatment, which could include rest, physical therapy, or even surgery. By using an MRI protocol to diagnose a sports hernia, doctors can provide their patients with a more precise and accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.

MRI Protocol for Sports Hernia Evaluation
MRI is an essential diagnostic tool for evaluating a sports hernia. This non-invasive imaging procedure allows medical professionals to get a clear and detailed view of the affected area. Through MRI, physicians can accurately diagnose the severity of the hernia and create a treatment plan accordingly.
The MRI protocol for a sports hernia evaluation typically involves imaging the lower abdomen and pelvis. An MRI scan may also include imaging of the hips and groin area to better evaluate the affected area. The MRI examination typically includes T1- and T2-weighted images, as well as fat-suppressed images. These images provide a detailed look at the soft tissues of the lower abdomen and pelvis, giving physicians an accurate representation of the hernia.
The MRI protocol for a sports hernia evaluation is designed to detect any damage to the abdominal wall, as well as any hernias present in the pelvic area. Additionally, the MRI can detect any tears in the abdominal muscles, which may cause pain and other symptoms. After an MRI is performed, the physician may review the images and formulate a treatment plan.
When evaluating a sports hernia, MRI is a reliable and non-invasive imaging procedure. The MRI protocol for a sports hernia evaluation allows physicians to get a detailed look at the affected area, enabling them to accurately diagnose the severity of the hernia and create an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Sports Hernia
Sports hernias are painful injuries that can significantly impact an athlete’s performance. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatment options available to help relieve the pain and discomfort associated with this condition. One of the most common treatments for sports hernias is an MRI protocol. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) enables medical professionals to get a clear picture of the injury and can help them diagnose and treat the hernia accordingly.
The MRI protocol typically involves the use of a contrast agent, which helps enhance the visibility of the tissues and organs in the body. Depending on the severity of the hernia, the MRI protocol may also require the use of an anesthetic or sedative to make the procedure more comfortable for the patient. The MRI protocol is an important part of the treatment process and can help medical professionals to accurately diagnose the hernia and determine the best treatment plan for the patient.
In addition to the MRI protocol, other treatments for sports hernias may include rest, physical therapy, and surgery. Rest is important in helping the hernia heal and can also help to reduce pain and discomfort. Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles that may have been weakened by the hernia, as well as improve the range of motion and flexibility of the affected area. Surgery is considered a last resort, but is sometimes necessary in order to repair the hernia or to prevent further damage.
Overall, the treatment plan for a sports hernia should be tailored specifically to the individual and based on the severity of the injury. The MRI protocol is an important part of any treatment plan, but other treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and surgery can also help to relieve pain and discomfort, as well as ensure a full recovery.
Prevention of Sports Hernia
Sports hernia is a debilitating sports injury that can have long-lasting repercussions. Taking precautionary measures to prevent it can save athletes from having to experience the pain and discomfort associated with the condition. Prevention is possible by following the right protocol as soon as any pain is felt in the lower abdominal area.
Athletes should first consult a physician to discuss the symptoms and possible causes. Following this, the doctor may recommend a sports hernia MRI protocol to accurately diagnose the condition. The MRI will show any deterioration of the muscles and tendons in the lower abdominal area that is causing the pain.
From there, the doctor may suggest a treatment plan to help the athlete prevent sports hernia from occurring. It is important to follow the plan to the letter, as improper management of the condition can lead to further damage to the affected muscles and tendons.
Athletes should also take proactive measures to prevent sports hernia. This includes warming up and stretching before and after exercise, avoiding activities that involve sudden movements, and using proper exercise technique. Wearing supportive footwear and a supportive belt around the affected area can also help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Taking the right steps to prevent sports hernia can help athletes stay healthy and active for longer. The key is to be aware of the signs and symptoms, seek professional medical advice when required, and follow the doctor’s recommended treatment plan. Doing so can help athletes prevent sports hernia from occurring and enjoy a pain-free life.
FAQs About the Sports Hernia Mri Protocol
Q1: What is a Sports Hernia MRI Protocol?
A1: A sports hernia MRI protocol is a type of imaging test that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose and monitor sports hernias. The MRI allows the doctor to create detailed images of the groin area to help identify the extent of the injury and guide treatment.
Q2: How is a Sports Hernia MRI Protocol performed?
A2: During a sports hernia MRI protocol, the patient lies on their back on the MRI table and the groin area is placed into the MRI machine. The MRI machine will then generate a detailed image of the area, which is then used to diagnose and monitor the injury.
Q3: Are there any risks associated with a Sports Hernia MRI Protocol?
A3: Generally, MRI scans are considered safe and there is no known risk associated with the procedure. However, due to the presence of a strong magnetic field, people with certain medical implants, such as pacemakers, may not be able to have the scan. Additionally, some people may experience anxiety while in the MRI machine.
Conclusion
Sports hernia MRI protocol is an important tool in diagnosing and treating sports hernia injuries. It can help to identify the location and size of the hernia, as well as any accompanying soft tissue damage. Additionally, the MRI can be used to monitor the healing process and determine whether any additional treatments are necessary. With the help of the MRI, athletes can identify and treat their hernia injuries early in order to return to full health and performance as quickly as possible.